- highlights improvements to clusterization algorithms, producing higher-quality meshlets and better partitioning for hierarchical structures
- stabilizes all experimental features with API, ABI, and behavior compatibility guarantees
- additionally announces the inclusion of clusterlod, a single header library for continuous level of detail generation

- details performance optimizations for a VR title on Quest 2
- describes improved culling and draw call reduction strategies
- presents solutions for reducing draw calls through manual instancing, Custom Primitive Data, and LOD bias techniques

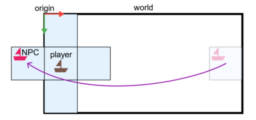
- discusses a simple world wrapping implementation using a chunk-based hierarchy in Godot
- presents a terrain LOD system with skirts to prevent cracks
- additionally presents tree impostors for distant vegetation using billboards
- presents a mesh-based reconstruction approach that jointly optimizes geometry and appearance through differentiable rendering
- uses restricted Delaunay triangulation to enforce connectivity and creates smooth surfaces with opaque triangles

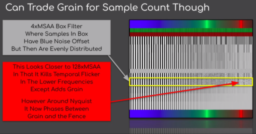
- The video discusses filtering considerations when implementing real-time graphics
- compares against cinema quality and presents what causes games to have a specific look
- additionally presents games that achieved particularly good results in image clarity
- The video presents how to update the texture projection logic so that it can better deal with horizontal slopes
- approaches the problem by projecting textures from the front and sides instead of only the top
- shows how to implement the technique in both Unreal and Unity visual scripting
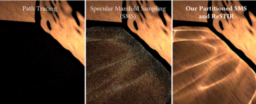
- extends Specular Manifold Sampling for interactive caustic rendering using tile-based sample space partitioning
- restricts expensive Newton iterations to the vicinity of seed paths by building per-frame prior distributions
- applies ReSTIR spatiotemporal resampling to amortize sample generation costs and achieve variance reduction
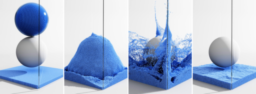
- introduces a novel incompressible SPH scheme using second-order implicit descent
- demonstrates improved incompressibility and stability compared to velocity-based methods like IISPH and DFSPH
- remains unconditionally stable even for large time steps while avoiding the compression artifacts of standard position-based methods
Thanks to Matt Pharr for support of this series.
Would you like to see your name here too? Become a Patreon of this series.