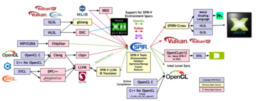
- blog post that looks back at Khronos Group’s 25-year history of enabling graphics programming across platforms
- traces the evolution from OpenGL and OpenGL ES through WebGL, Vulkan, and OpenXR to modern standards like Slang for neural rendering
- closes with a look at the next years of collaboration

- comprehensive walkthrough of implementing halftone effects as shaders from basic circular dot grids to advanced variants
- explores multichannel halftoning with RGB and CMYK color separation
- presents techniques for breaking grid constraints, enabling surface tension effects
- additionally shows how to integrate interactivity

- recording of a live stream showing a walkthrough on how to update a Vulkan app to use the new Descriptor Heaps extension
- showing the necessary definitions in the spec and how to integrate it into an application
- tutorial on using the Vulkan compute‑shader pipeline to render a Shadertoy‑style by integrating compute work into the application
- walk-through covers all the required pieces of the API and how they interact
- full source code is available

- explores using small multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) to encode graphics data like radiance, irradiance, depth, and BRDF information
- compares MLP-based encoding against traditional methods like Spherical Harmonics
- discusses trade-offs in storage size and quality, as well as implementation challenges

- documents insights from building an immediate-mode GUI library
- covering interactions and layout logic as well as rendering constraints
- presents a tile-based SDF-based renderer to dispatch specialized shaders for improved occupancy
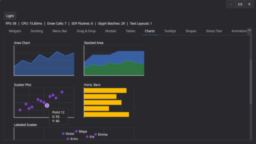
- presents an updated Sponza glTF model with cleaned-up uncompressed PNG textures
- compares AVIF texture compression with runtime GPU compression via Spark against precompressed KTX formats
- demonstrates memory and quality comparisons
- announces the formation of a Ecma Technical Committee to standardize HLSL as a cross-platform shader language
- traces HLSL’s evolution from DirectX 9, DXC, Clang integration, and the importance of Google’s SPIRV code generation contributions
- commits to public development on GitHub with conformance test suite

- details progress on Clang HLSL implementation, including improved root signature diagnostics
- explains the rationale behind standardizing HLSL through Ecma TC 57 to address cross-platform shader build pipeline complexity and quality issues
- announces new features to combine Cooperative Vector and Wave Matrix capabilities for efficient neural network evaluation in shaders
- implements AMD’s FidelityFX Single Pass Downsampler for Apple Metal API, generating depth pyramid mipmaps in one compute pass
- explains threadgroup organization with 16×16 threads processing 64×64 pixels using threadgroup memory to avoid device memory round-trips
- presents an adaptive sampling and denoising pipeline designed for less than one sample per pixel path tracing systems
- introduces stochastic sample placement formulation enabling gradient estimation
- demonstrates consistent improvements over uniform sparse sampling, particularly in reconstructing specular highlights and shadow boundaries using tonemapping-aware training

- analyzes Michael Abrash’s hand-crafted x86 assembly optimizations in Quake’s software renderer
- details key techniques including FPU pipeline parallelization, hiding multiplication latency, self-modifying code, and overlapping FDIV with integer pipelines

- derives mathematical equations for estimating stopping/starting times and distances from critical spring damper character movement systems
- uses Lambert W function (product logarithm) to solve for stopping times from spring parameters
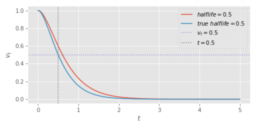
- presents methods to fit spring half-life parameters from measured animation data, including “true half-life” definition based on exact halfway-point timing
Thanks to Aras Pranckevicius for support of this series.
Would you like to see your name here too? Become a Patreon of this series.